Why It’s Important to Get Regularly Vaccinated as an Adult

Many people think that vaccines are only for children, but the truth is that adults also need to be vaccinated periodically to prevent serious illnesses, avoid hospitalizations, and care for the health of the community. Do you know which vaccines you should receive as an adult? Are you aware of the benefits of staying up-to-date with your vaccination schedule? Do you have doubts or fears about vaccines?
In this blog, we will tell you everything you need to know about vaccination in adults: why it is important, which vaccines you should receive, and what myths circulate about vaccines.
Keep reading and discover how to protect yourself and others with a simple injection.
Why get vaccinated as an adult?
Vaccination in adulthood is essential to prevent serious consequences of preventable diseases such as flu, pneumonia, tetanus, diphtheria, hepatitis B, and meningitis.
Vaccination also helps prevent complications that can be very serious, especially in older adults and those with chronic diseases. People with chronic conditions like diabetes, heart and lung diseases, and HIV/AIDS are at higher risk of severe consequences of preventable diseases if they are not vaccinated.
Additionally, vaccination also protects the community at large, especially those who cannot be vaccinated, such as babies and people with weakened immune systems. By keeping our vaccination schedule up to date, we can contribute to preventing the transmission of diseases and protecting the most vulnerable.
Recommended vaccines for adults
There are several vaccines specifically recommended for adults, depending on their age, vaccination history, and health conditions. Some of the recommended vaccines include:
- Influenza vaccine: recommended every year for everyone aged 6 months and older.
- Tetanus and diphtheria (Td) vaccine: recommended as a booster every 10 years.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine: recommended for adults under 26 who have not completed the vaccine series as teenagers.
- Hepatitis B vaccine: recommended for those at high risk of infection, such as healthcare workers, people with chronic liver disease, and those engaging in unprotected sex with an infected person.
- Pneumococcal vaccine: recommended for adults aged 65 and older and those with certain chronic diseases.
- Meningococcal vaccine: recommended for adults at high risk of infection, such as those with weakened immune systems.
- COVID-19 vaccine: recommended for everyone aged 12 and older to prevent COVID-19 and severe illness or death from the disease.
- Shingles (herpes zoster) vaccine: recommended for adults aged 50 and older to prevent shingles and its complications.
- Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine: recommended for adults aged 18 to 24 who did not receive the vaccine as children, especially in women of childbearing age.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine which vaccines are suitable for each person, considering their vaccination history and personal risk factors.
Benefits of regular vaccination as an adult
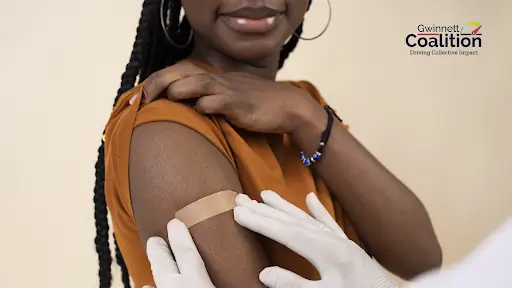
Regular vaccination as an adult has several important benefits, including:
Protection against serious diseases: Vaccines help prevent diseases such as COVID-19, flu, pneumonia, tetanus, and hepatitis B. These diseases can cause complications that may require hospitalization or even lead to death.
- Protection of vulnerable individuals: Some people cannot be vaccinated or have a weak immune response to vaccines, such as babies, older adults, and those with certain chronic diseases. By getting vaccinated, adults also help protect these vulnerable individuals by reducing the risk of transmitting diseases to them.
- Prevention of outbreaks: Vaccines help prevent the transmission of infectious diseases in the community, which can prevent outbreaks and pandemics. When a large portion of the population is vaccinated, herd immunity is created, making it difficult for diseases to spread.
- Cost savings: Infectious diseases can be costly to treat and can affect people’s quality of life. By preventing these diseases through vaccination, adults can save money on medical expenses and avoid losing time from work or study.
Remember that vaccination benefits not only individuals, but also society as a whole. By getting vaccinated regularly, adults can contribute to preventing infectious diseases and protecting the most vulnerable people.
Debunking common myths about vaccines
There are many myths and misunderstandings about vaccines that have generated distrust and resistance to vaccination. Here are some of the most common myths, along with facts and data to refute them:
Myth: Vaccines cause autism.
Reality: There is no scientific evidence supporting this claim. A now-retracted study that once suggested a link between the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and autism was debunked by the medical journal that published it due to design flaws and author conflicts of interest.
Myth: Vaccines can weaken the immune system.
Reality: Vaccines act by stimulating the immune system to produce an immune response against a specific disease, strengthening rather than weakening the immune system.
Myth: Infectious diseases are a thing of the past and are no longer a problem.
Reality: Although many infectious diseases are less common today thanks to vaccination, they remain a public health risk and can resurge if vaccination rates decline.
Myth: Vaccination is only for children.
Reality: Vaccination is important for all ages, including adults. Some adults may need booster doses to maintain protection against infectious diseases.
Myth: Vaccines can cause serious side effects.
Reality: Vaccine side effects are generally mild and temporary, such as pain at the injection site or low-grade fever. Serious side effects are very rare, and the potential benefits of vaccination far outweigh any possible risks.
As an adult, it’s crucial to inform yourself about the facts and break the chain of misinformation about vaccines so that you and your loved ones can make informed decisions about your health and the health of your community.
In conclusion, regular vaccination is essential for maintaining good health and preventing diseases. Moreover, by getting vaccinated, we are also protecting our communities. Therefore, we encourage you to roll up your sleeve for Gwinnett and get vaccinated if you haven’t already.
Consult with your doctor and ensure you are up-to-date on your vaccines to enjoy a healthy life. Together, we can keep Gwinnett healthy and safe!
What We Do
© 2023 Gwinnett Coalition. All Rights Reserved
